OET Strategies
OET Listening: Understanding the Exam Format and Sections
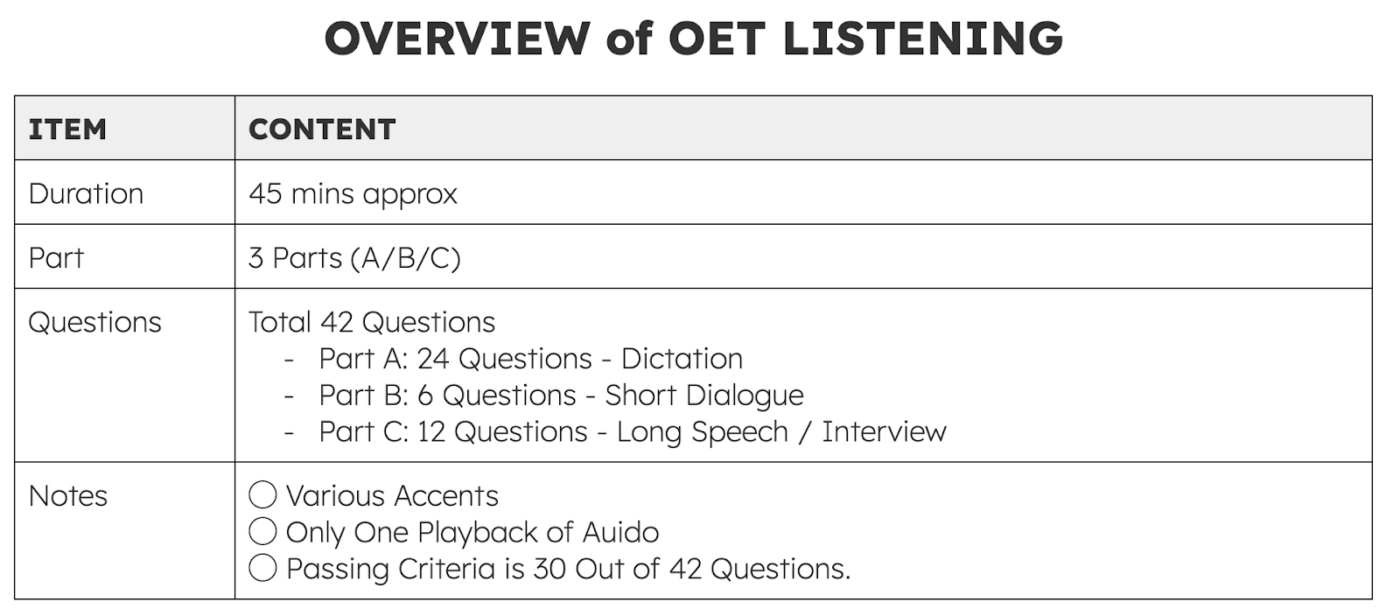
OET Listening assesses whether you can accurately understand spoken English used in real healthcare environments.
For doctors and nurses preparing to work abroad, this section reflects the kind of communication you will hear every day in clinical settings.
In this article, we will look closely at the structure and characteristics of each part of the Listening test, as well as how the overall format shapes the skills being assessed.
Understanding what to expect can make your preparation feel more focused and practical.
Let’s begin by reviewing the overall structure of OET Listening.
One of the defining features of OET Listening is its use of realistic conversations based on actual clinical situations.
Unlike IELTS or TOEFL, which often emphasize academic topics, OET centers on workplace-oriented communication.
The language used is practical and clinically relevant, focusing on how information is exchanged in healthcare settings. This includes not only medical vocabulary, but also the way professionals explain conditions, discuss care plans, and clarify concerns with patients and coworkers.
The recordings also contain everyday idioms and common collocations, making the style more conversational than academic. This reflects how English is actually spoken in hospitals and clinics, where communication tends to be clear, direct, and natural rather than formal or theoretical.
Because OET originated in Australia, Australian English accents appear frequently in the audio. These accents are generally clear and not overly strong or unusual. With a solid foundation in English listening, most candidates can adapt without major difficulty.
The goal is not to test unfamiliar accents, but to reflect the variety of English you may encounter in real healthcare workplaces.
With this overall picture in mind, let’s now take a closer look at each part of the Listening section and how it is structured.
Breakdown of Each Listening Part
Below is a summary of how each part of the OET Listening section is structured.
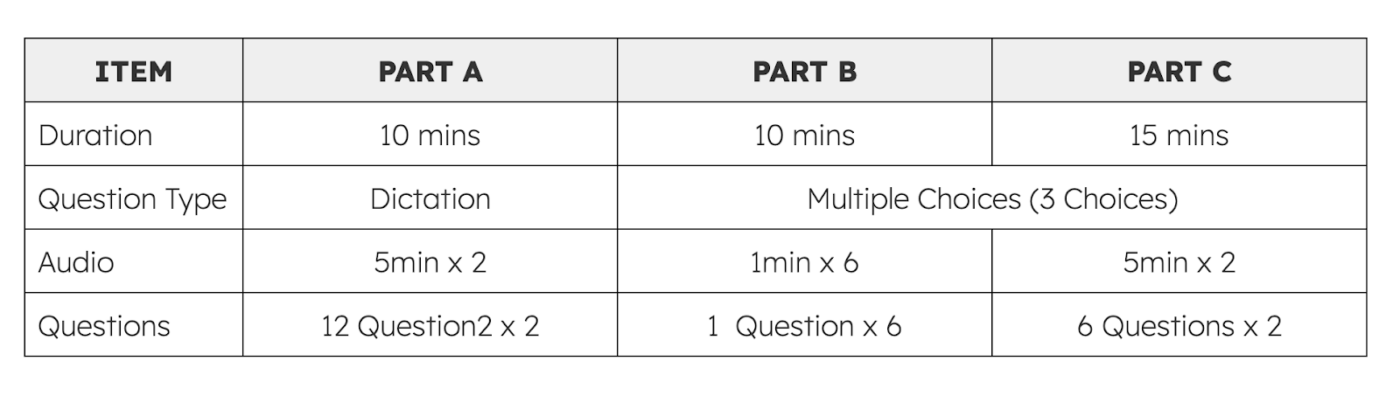
Part A: Patient Consultations
Part A focuses on consultations between a healthcare professional and a patient. You listen to a conversation and complete clinical notes based on what you hear. This format mirrors real-life tasks such as documenting symptoms, medical history, and key concerns.
This part tests more than vocabulary. It also assesses your ability to identify key information quickly and record it accurately. You must follow the flow of the conversation, recognize clinically important details, and capture them in written form under time pressure.
Parts B and C: Workplace Communication
Parts B and C involve listening to workplace communication, such as handovers, explanations, or short professional talks. After listening, you choose the most appropriate answer from three options.
These parts require more than simply picking out keywords. You need to understand the overall message and the speaker’s main point. This reflects real clinical communication, where meaning often depends on context, tone, and the purpose of the discussion, not just individual words.
A Key Feature: Dictation-Style Tasks
One major feature of OET Listening is that dictation-style tasks make up more than half of the section. This means you are often required to write down information based on what you hear, rather than just selecting multiple-choice answers.
Because dictation is not commonly emphasized in English education, many candidates initially find this format challenging. It requires careful listening, accurate spelling, and quick processing of spoken information. For busy healthcare professionals, this can feel demanding at first.
However, the task patterns are relatively consistent. The types of information you are asked to record, such as symptoms, durations, and key clinical details, follow predictable formats. With repeated, focused practice, significant score improvement is very achievable.
This reflects an important aspect of OET: it does not aim to trick candidates. Instead, it evaluates whether you can handle realistic listening tasks that resemble everyday clinical responsibilities.
Watch the Video
Prefer video? Here’s a quick walkthrough of this article.
Study with OET BANK
Stop wasting time comparing OET materials.
With OET BANK, you get:
- Premium-quality OET materials, built by professionals
- A focused, efficient study path — no unnecessary content
- A system designed to help you pass OET once — without trial and error
If you want to prepare properly and pass with confidence,
you don’t need to look anywhere else.
Pick your materials and start today — with OET BANK.




